Compare proband vs. control
The first step is to input the number of dicentrics and the number of cells counted for the proband (case) and for the control. A significant P-value suggests that the proband was exposed two a dose () and the calculation of the dose shall be performed if an appropriate calibration curve is available.
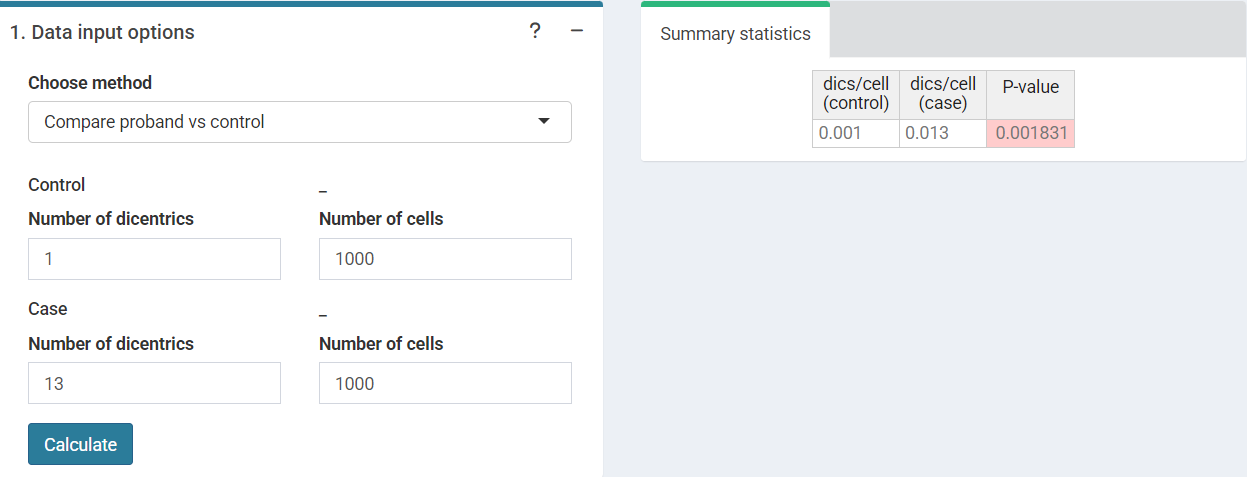
‘Data input options’ in the characteristic limits module - Compare proband vs control method.
This step is accomplished in R by poisson.test()
function:
control_data <- c(aberr = 1,
cells = 1000)
proband_data <- c(aberr = 13,
cells = 1000)
result_data <- matrix(c(
control_data["aberr"] / control_data["cells"],
proband_data["aberr"] / proband_data["cells"],
stats::poisson.test(c(proband_data["aberr"], control_data["aberr"]),
c(proband_data["cells"], control_data["cells"]))$p.value
), ncol = 3, nrow = 1)
colnames(result_data) <- c("dics/cell (control)", "dics/cell (case)", "P-value")
result_data
#> dics/cell (control) dics/cell (case) P-value
#> [1,] 0.001 0.013 0.001831055Characteristic limits
The user can choose the type I error rate()(false positive rate) and the type II error rate () (false negative rate).
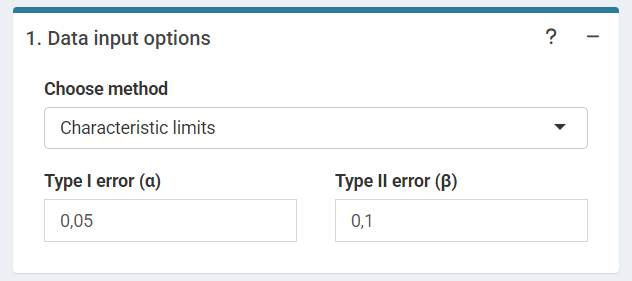
‘Data input options’ in the characteristic limits module - Characteristic limits.
The input data are: the number of dicentrics and cells of the control
data if
()
is selected or the mean number of dicentrics per cell if
()
is selected. Input the pre-calculated curve in .rds format
obtained in the dose-effect fitting module.
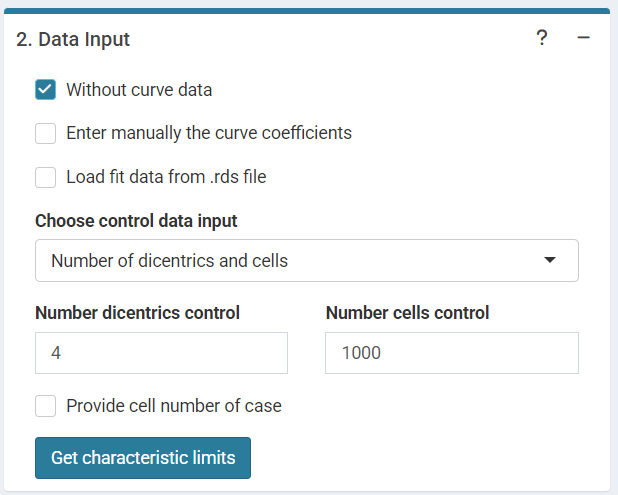
‘Data input options’ in the characteristic limits module - Characteristic limits - Without curve data option.
or input the curve coefficients manually in case the user wants to use a pre-existing curve calculated outside of Biodose Tools.
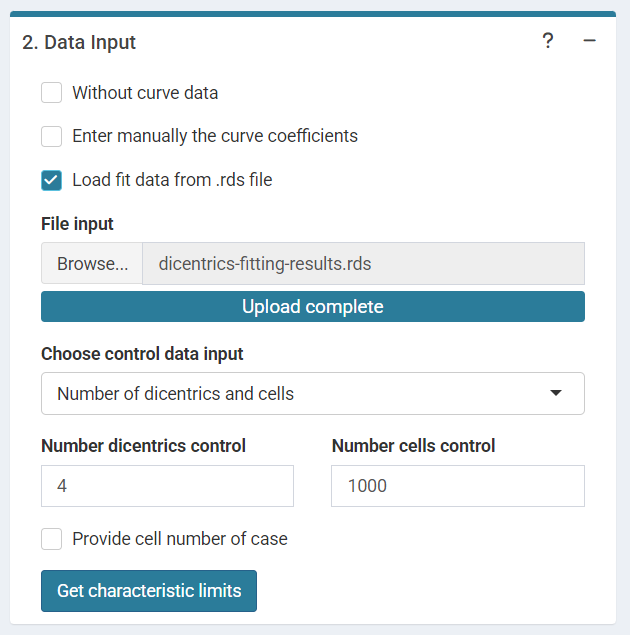
‘Data input options’ in the characteristic limits module - Characteristic limits - Loaded data .rds option.
If these information is not available, choose () and the dose will not be calculated.
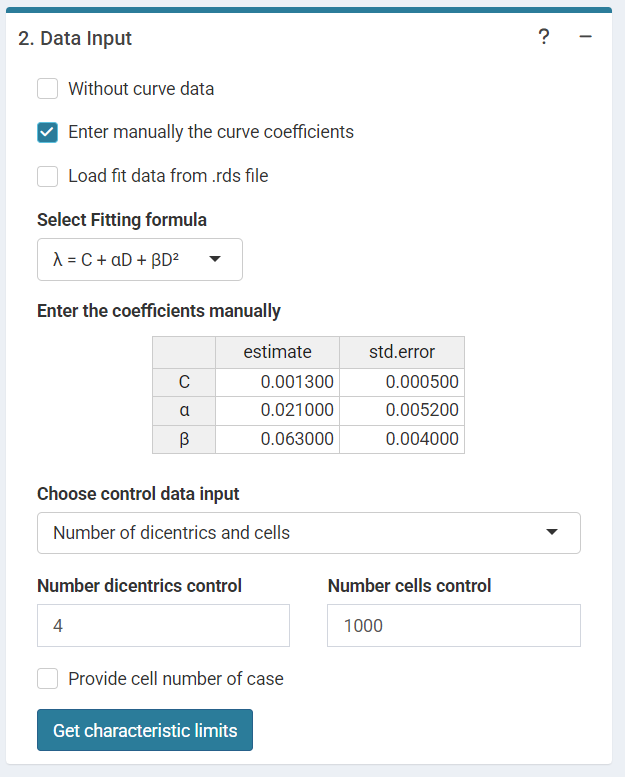
‘Data input options’ in the characteristic limits module - Characteristic limits - Manually entered curve data option.
This step is accomplished in R by calling the
calculate_characteristic_limits() function that gives the
decision threshold and the detection limit:
cells_proband <- c(20, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000)
control_data <- c(aberr = 4,
cells = 1000)
c_limits <- sapply(cells_proband, function(x) calculate_characteristic_limits(
y0 = control_data["aberr"],
n0 = control_data["cells"],
n1 = x,
alpha = 0.05,
beta = 0.1,
ymax = 100,
type = "var"
))
c_limits
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6]
#> decision_threshold 1 1 2 3 7 12
#> detection_limit 3.88972 3.88972 5.32232 6.680783 11.77091 17.78159For the Minimum resolvable dose
()
and the Dose at detection limit
()
project_yield() function is applied:
fit_results_list <- system.file("extdata", "dicentrics-fitting-results.rds", package = "biodosetools")%>%
readRDS()
fit_coeffs <- fit_results_list$fit_coeffs[, "estimate"]
est_dec <- sapply((unlist(c_limits["decision_threshold", ]) + 1) / cells_proband, function(x) project_yield(
yield = x,
type = "estimate",
general_fit_coeffs = fit_coeffs,
general_fit_var_cov_mat = NULL,
protracted_g_value = 1,
conf_int = 0))
est_det <- sapply(unlist(c_limits["detection_limit", ]) / cells_proband, function(x) project_yield(
yield = x,
type = "estimate",
general_fit_coeffs = fit_coeffs,
general_fit_var_cov_mat = NULL,
protracted_g_value = 1,
conf_int = 0))
est_dec
#> [1] 1.0956559 0.6344613 0.5284423 0.4030546 0.3443595 0.2954731
est_det
#> [1] 1.5918121 0.9474389 0.7560874 0.5662469 0.4503848 0.3712934Results are displayed in the UI as a table and can be saved in .csv and .tex
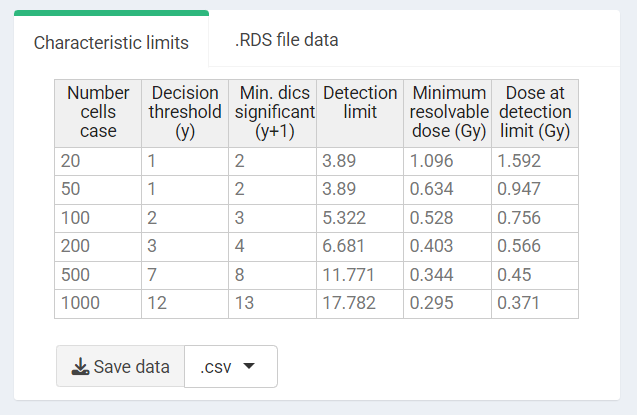
‘Results’ tabbed box in the characteristic limits module - Characteristic limits.
